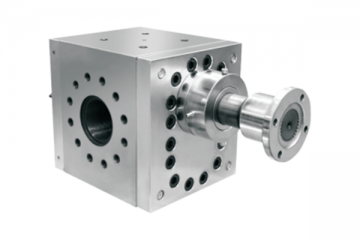
The core principle for adjusting the working pressure of a reactor melt pump is “flow control, resistance reduction, and parameter matching,” primarily achieved through process adjustments, equipment parameter settings, and pipeline optimization.
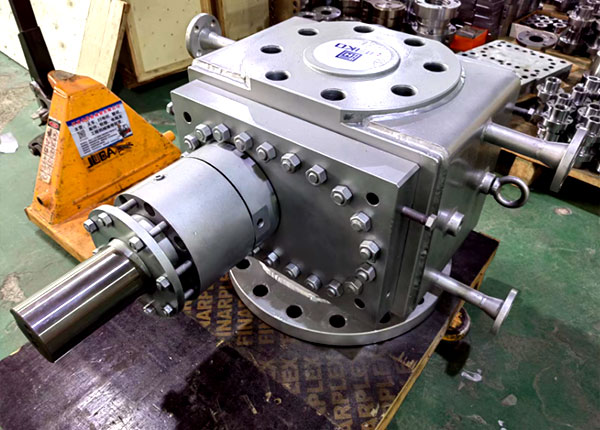

Core Adjustment Methods
Adjusting pump speed: Use a variable frequency drive to alter motor speed. Increasing speed boosts flow rate while simultaneously raising outlet pressure. Reducing speed lowers pressure, representing the most direct and commonly used method.
Control downstream resistance: Adjust the opening of the outlet pipeline control valve. Closing the valve increases pipeline resistance, raising pump outlet pressure; opening the valve reduces resistance and lowers pressure. Indirect adjustment is also possible by modifying feed resistance in downstream equipment (e.g., molds, heat exchangers).
Matching Equipment and Process Parameters:
Replace gear sets with different module and tooth widths to alter the pump's pressure-bearing capacity. Adjust the pump body heating temperature based on material viscosity to reduce flow resistance and indirectly stabilize pressure.
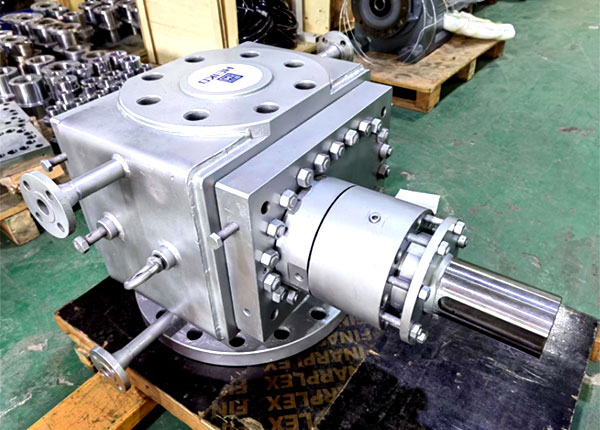

Adjusting Feed Conditions:
Optimize feed pressure or vacuum levels within the reactor to reduce the pump's inlet pressure differential burden and prevent outlet pressure instability caused by inlet pressure fluctuations.
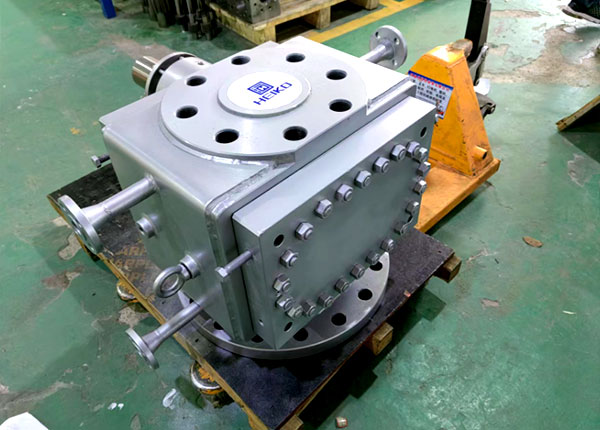

Adjustment Precautions
Operate adjustments gradually to prevent sudden pressure surges or drops, which may damage pump seals or gear structures.
Pressure regulation must align with flow requirements; do not prioritize high pressure at the expense of flow stability.
If material viscosity changes occur, synchronously adjust pump heating temperature to ensure material fluidity meets pressure regulation demands.